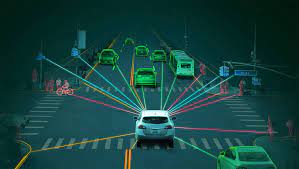
Introduction
Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous or driverless cars, represent a transformative technology poised to reshape the future of transportation. While the promise of increased safety and efficiency is captivating, the journey towards fully autonomous vehicles is not without challenges and complexities, raising questions about the societal, ethical, and technological implications.
Technology Behind Self-Driving Cars
The technology driving self-driving cars is multifaceted. It relies on an intricate combination of sensors, cameras, lidar, radar systems, and advanced artificial intelligence algorithms. These components work in tandem to perceive the vehicle’s surroundings, interpret data, and make real-time decisions.
Levels of Automation
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines levels of automation from 0 to 5, ranging from no automation to full automation. Understanding these levels helps contextualize the capabilities and limitations of self-driving technology. Currently, most self-driving systems are at levels 2 or 3, where the vehicle can handle certain driving tasks but requires human intervention.
Promise of Self-Driving Cars
The potential benefits of self-driving cars are extensive. Improved safety through the reduction of human error, decreased traffic congestion, enhanced accessibility for individuals with mobility challenges, and increased efficiency and productivity are among the promises that fuel the excitement surrounding autonomous vehicles.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite the promises, self-driving cars face significant challenges. Technical hurdles, ethical and legal dilemmas, cybersecurity risks, and the need for extensive infrastructure modifications present obstacles to the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles.
Testing and Regulatory Landscape
The testing and regulatory landscape for self-driving cars is evolving. Rigorous testing protocols, regulatory frameworks, and collaboration between governments and industry players are essential components to ensure the safe development and deployment of autonomous vehicles.
Public Perception and Acceptance
Public perception and acceptance play a crucial role in the successful integration of self-driving cars. Building trust in autonomous technology, addressing cultural and psychological factors, and implementing public education initiatives are necessary to garner support and understanding.
Industry Players and Innovations
Several companies are at the forefront of self-driving technology, pushing the boundaries of innovation. From leading automakers to tech giants, ongoing research and development efforts continue to bring forth breakthroughs in the field of autonomous vehicles.
Environmental Impact
Self-driving cars have the potential to contribute to environmental sustainability. Through optimized routes, reduced traffic congestion, and the potential shift to electric and alternative fuel vehicles, autonomous transportation could play a role in mitigating emissions and fostering sustainable transportation solutions.
The Road Ahead: Future of Self-Driving Cars
The future of self-driving cars holds exciting possibilities. Continued technological advancements, integration with smart city infrastructure, and the evolution of the transportation ecosystem are expected to shape the trajectory of autonomous vehicles in the years to come.
Conclusion
The promise and challenges of self-driving cars represent a delicate balance between innovation and responsibility. As technology continues to progress, addressing concerns, building public trust, and navigating regulatory landscapes will be crucial in realizing the potential benefits of autonomous transportation. The road ahead for self-driving cars requires a collaborative effort to ensure a safe, efficient, and inclusive future.