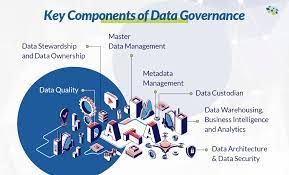
In the digital age, where data has become a strategic asset for businesses, the art of data governance has emerged as a critical discipline. Data governance goes beyond mere management; it involves establishing policies, processes, and standards to ensure data quality, integrity, and security. In this exploration, we delve into the intricacies of data governance and its transformative impact on organizations.
Clear Accountability
Data governance begins with establishing data ownership. Clear accountability ensures that individuals or teams are responsible for the quality, accuracy, and security of specific datasets. This ownership creates a foundation for effective data management.
Defining Responsibilities
Defining responsibilities is integral. Data stewards, individuals entrusted with data oversight, play a key role. They define and enforce data-related policies, ensuring adherence to data governance principles across the organization.
Data Quality Standards
Defining data quality standards is paramount. Data governance involves setting clear criteria for data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. This ensures that organizations maintain a high standard of data quality.
Security and Privacy Policies
Security and privacy policies are critical components. Data governance addresses the protection of sensitive information through the establishment of robust security measures and compliance with privacy regulations.
COBIT Framework
Implementing a framework is a best practice. The COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) framework is widely adopted for data governance. It provides a comprehensive set of guidelines for effective data management and control.
Data Management Maturity Models
Data management maturity models guide organizations. These models, such as the Data Management Body of Knowledge (DAMA-DMBOK), help businesses assess their current data management practices and progress toward higher maturity levels.
Breaking Silos
Collaboration across departments is crucial. Data governance breaks silos by fostering collaboration between IT, business units, legal, and compliance teams. This cross-functional approach ensures a holistic and integrated data governance strategy.
Communication and Training
Communication and training are key elements. Effective data governance involves clear communication of policies and standards throughout the organization. Training programs ensure that employees understand their roles in maintaining data quality and security.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Improved decision-making is a direct result. Data governance ensures that decision-makers have access to accurate and reliable data. This promotes data-driven decision-making, enhancing the overall effectiveness of strategic initiatives.
Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation is a significant benefit. Data governance identifies and addresses data-related risks, reducing the likelihood of errors, inaccuracies, or security breaches that could impact the organization’s reputation and operations.
Consistency and Accuracy
Enhanced data quality is a fundamental outcome. Data governance establishes standards for data consistency and accuracy. This, in turn, improves the reliability of reports, analyses, and business intelligence generated from the data.
Trust in Data
Building trust in data is crucial. When data is governed effectively, stakeholders can trust its accuracy and relevance. Trustworthy data fosters confidence in decision-making and enhances collaboration across departments.
Rigorous Policies vs. Agile Needs
Balancing rigor and flexibility is a challenge. While rigorous data policies are necessary for governance, organizations must also remain agile to adapt to evolving business needs and technological advancements.
User Adoption Challenges
User adoption challenges may arise. Resistance to new data governance processes or tools can impede successful implementation. Overcoming these challenges requires effective change management and user training.
AI and Automation Integration
Integration with emerging technologies is the future. Data governance will increasingly leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and automation for tasks such as data quality monitoring, anomaly detection, and policy enforcement.
Blockchain for Data Integrity
Blockchain will play a role. As concerns about data integrity grow, blockchain technology may be integrated into data governance frameworks to provide transparent and tamper-proof records of data transactions.
Conclusion
Data governance is not just a compliance necessity; it’s an art form that shapes how organizations manage, utilize, and protect their most valuable asset—data. By establishing clear ownership, defining robust policies, and fostering collaboration across departments, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data. The impact extends beyond improved decision-making and enhanced data quality to building trust in data and mitigating risks. While challenges exist in finding the right balance and ensuring user adoption, the future of data governance holds exciting possibilities with the integration of emerging technologies. As organizations continue to evolve in the digital landscape, mastering the art of data.